GeoPub get-togethers provide an opportunity for geoscientists to catch up on the industry “goss”, have a few drinks, talk technical, reminisce, and/or generally socialise.
GeoPub Melbourne, which was launched only recently, has moved to a larger venue due to its immediate success! GeoPub Melbourne will now be held at P.J. O’Briens at Southbank
Every second Friday of the month, GeoPub Melbourne aims to become a regular event on any geologist’s social calendar.
Contact geopubmelb@gmail.com for further information.

Questions from several members prompted analysis of latest AIG Australian Geoscientist Employment Survey data to examine which fields of practice have been affected most by the prolonged downturn in geoscientist employment.
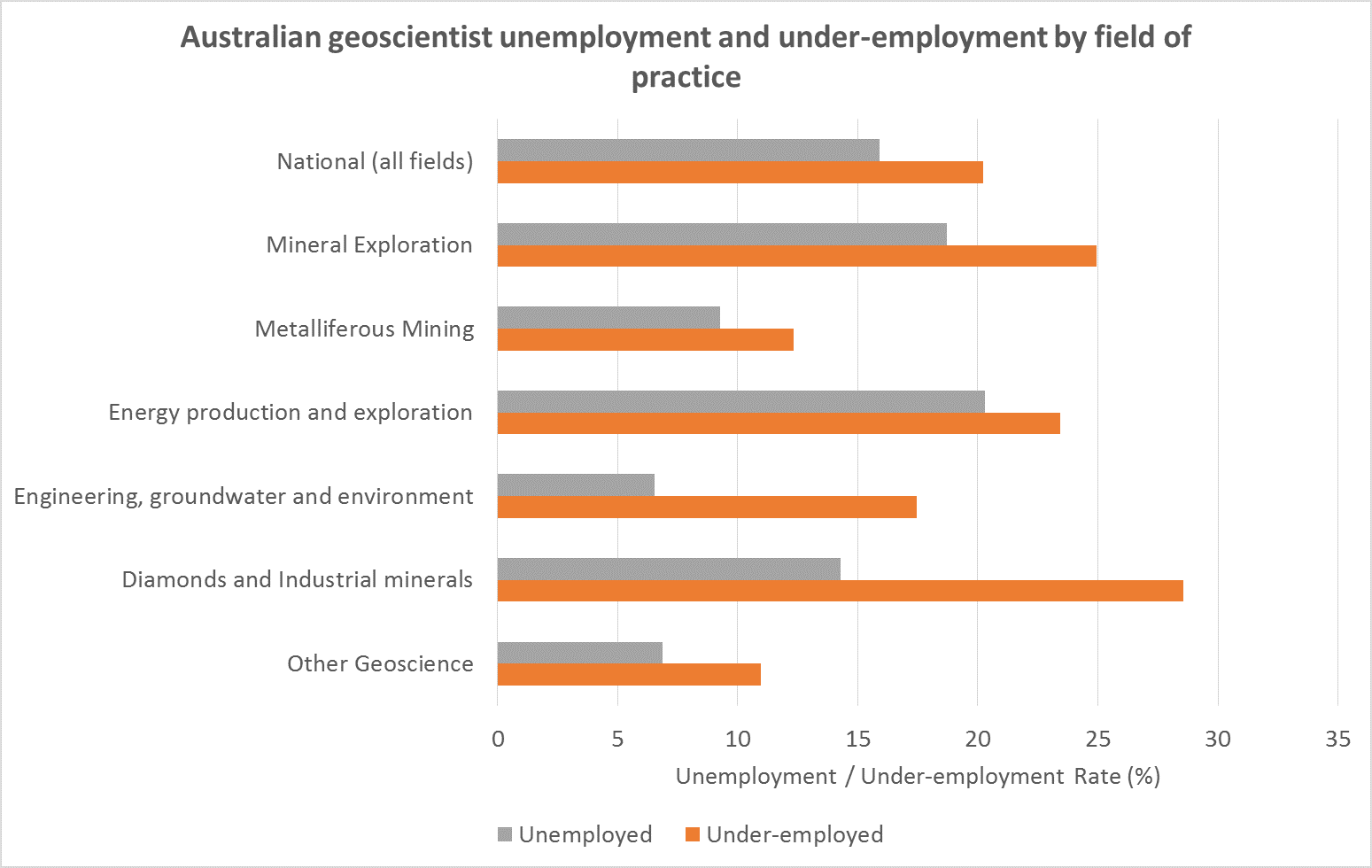
The survey revealed an unemployment rate of 15.9% and under-employment rate of 20.2% amongst geoscientists nationally. These rates were down from 19.5% and 23.4% respectively in the March quarter 2016 survey.
In the latest survey, the highest rate of unemployment was found to be amongst geoscientists seeking work in energy resource exploration and production (coal, coal seam gas and petroleum) at 20.3%, followed by mineral exploration, the largest geoscientist employment sector in Australia, at 18.7%.
The lowest rate of unemployment was found to affect geoscientists seeking work in engineering, environmental and groundwater resource geoscience at 6.5%.
Unemployment in all geoscience fields exceeded the average for the entire Australian workforce of 5.7% for June 2016.
The jobs outlook for Australia’s geoscientists has shown the first small signs of improvement in two years with the number of professional geoscientists in Australia seeking work or unable to secure satisfactory self-employment, falling fell in the June quarter compared with the preceding period.
This is the first sign of any improvement in the sector – hard hit by the retreating mining resources boom – since September 2014 but the outlook remains dire with higher numbers looking to leave the profession for opportunities elsewhere. The profession’s latest survey shows that at 30 June 2016, the unemployment rate amongst Australian geoscientists was 15.9% and the under- employment rate was 20.2%. This, compared with 19.5% and 23.4% respectively as at 31 March (Figure 1).
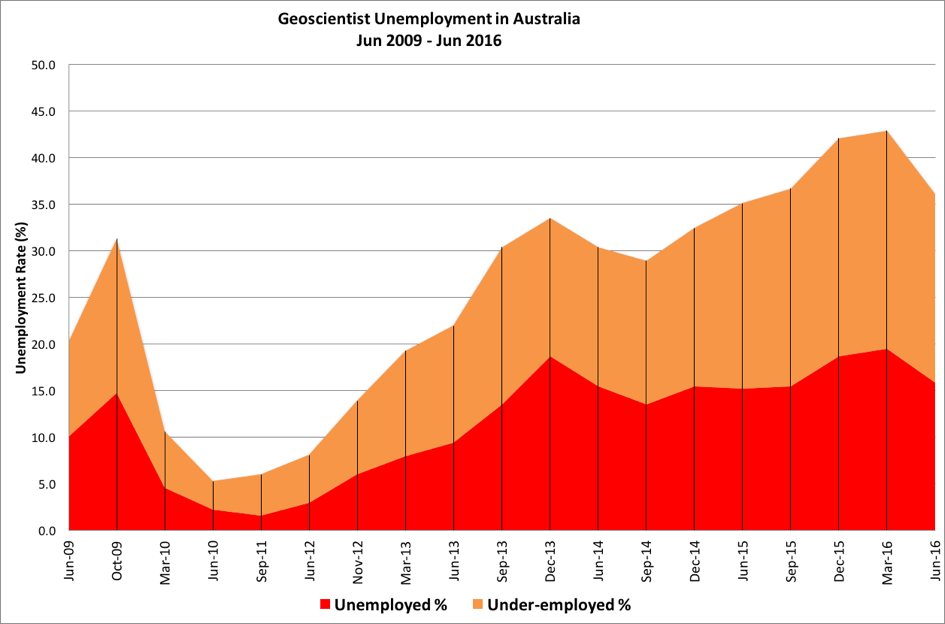
Figure 1. Geoscientist unemployment and under-employment in Australia June 2009 – June 2016
This is the first decline in both the unemployment and under-employment rates for geoscientists since September 2014. Even with the decline, however, the unemployment rate remains above that recorded by this survey in September 2015.
Almost half of Australia’s self-employed geoscientists were unable to secure more than one quarter of their desired workload during the quarter, pointing to a real unemployment rate of 27.6%, which decreased from 33.3% in the previous quarter.
The survey received 1095 responses this quarter from an estimated 6,000 geoscientists in Australia, working in all sectors of exploration and mining, government, education, research, environment and a range of other fields of practice.
On a state by state basis, decreases in both unemployment and under-employment were evident in all states except South Australia where unemployment remained static but under-employment amongst self-employed geoscientists increased (Figure 2). South Australia also recorded the highest combined rate of unemployment and underemployment, followed by Queensland and New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory. The combined unemployment and underemployment rate was very similar for Western Australia and Victoria, which recorded the greatest improvement during the quarter (Figure 3).
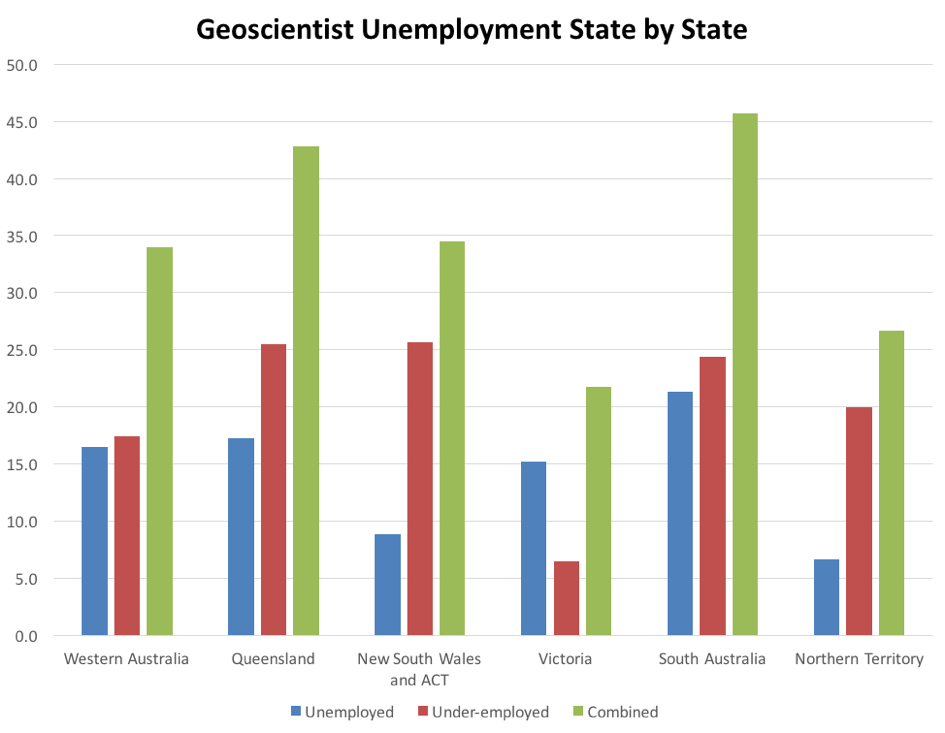
Figure 2. Geoscientist unemployment and underemployment by State
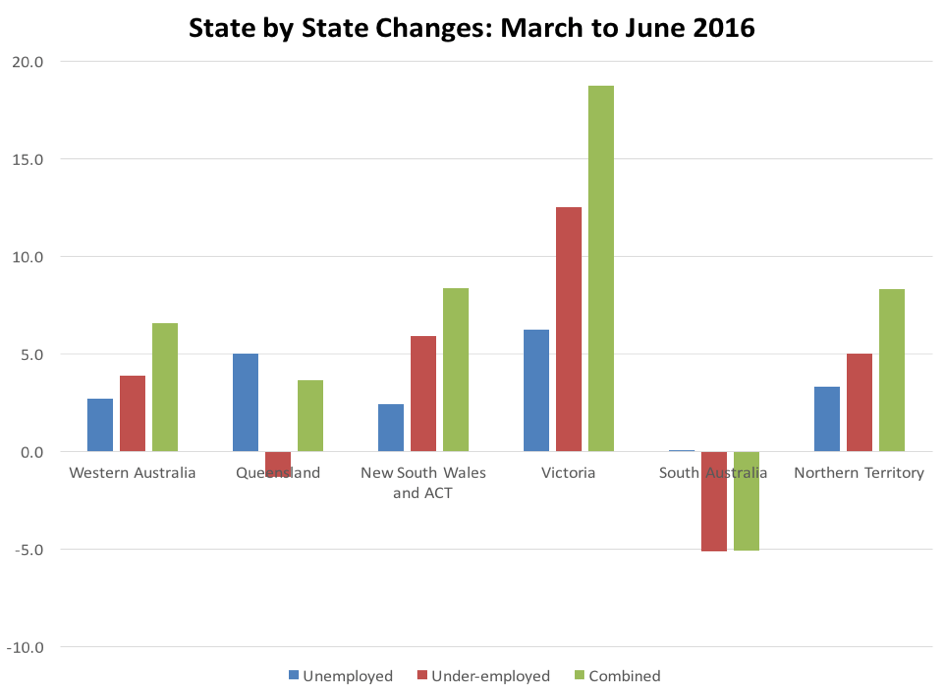
Figure 3. Changes in state unemployment and underemployment during Q2 2016
Long-term unemployment remains a key concern with the proportion of geoscientists who have been without work for more than 12 months increasing from 49% to almost 60% in the current survey.
Just over 70% of unemployed and underemployed respondents were not confident of regaining employment within the next 12 months.
Both figures reflect a further loss in confidence regarding employment prospects amongst geoscientists seeking work.
Almost 16% of unemployed and under-employed geoscientists indicated that they were seeking to leave the profession for roles with better employment prospects, up 2% from the previous quarter (Figure 4).
Some 13% of respondents currently in employment felt at risk of losing their jobs in the next three months: a slight decrease on the 15% recorded in March 2016.
The proportion of employed geoscientists in full time roles fell from 81% in March to 77% in this survey. The proportion of survey respondents in employment describing themselves as self- employed increased from almost 15% in March to over 16% in this survey.
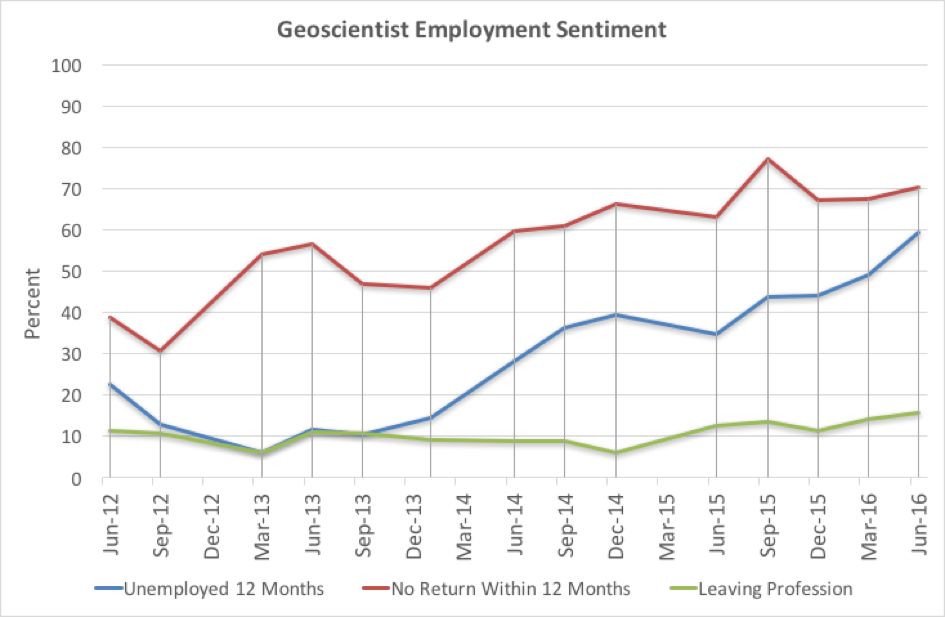
Figure 4. How Australia’s unemployed and underemployed geoscientists view their prospects
The June survey, for the first time, questioned respondents currently in employment on the type of employment in which they are engaged. The results confirmed the importance of the junior mining and exploration sector and small consulting/contracting groups which provided 27.1% and 19.6% of roles respectively – almost 47% of all geoscientist jobs in Australia (Figure 5). This is frequently overlooked by both Federal and State governments whose focus is frequently directed to larger participants in the industry. Major exploration and mining companies (e.g. Vale, BHPB, Rio Tinto) employ only 19% of geoscientists in Australia – significantly fewer than their junior competitors.
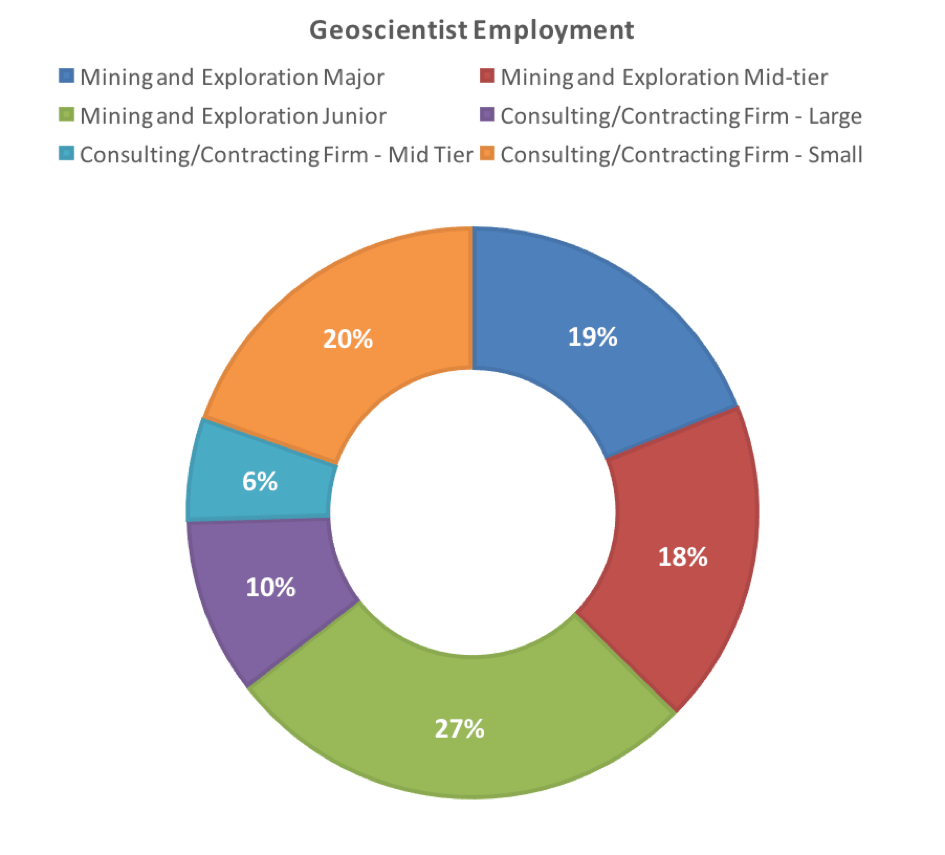
Figure 5. Geoscientist employment by enterprise type
AIG President, Mr Mike Erceg, described the results as mixed. “Any improvement in geoscientist employment prospects following such a prolonged downturn can only be described as very welcome news” Mr Erceg said. “We need, however, to see improvement in the unemployment and under-employment rates over more than a single quarter before becoming too excited by the prospect of a turnaround in geoscientist employment opportunities.” Mr Erceg said.
“The improvements evident in the latest survey confirm the anecdotal evidence of a very modest increase in exploration activity which seemed to gather momentum during the second quarter of this year. The improvement, however, brought a sharp increase in the proportion of long term unemployed geoscientists which is of real concern to the AIG which has been doing whatever it can to help members maintain and improve their skills and employment prospects.
“Initiatives have included allowing unemployed and under-employed members to defer membership fees and providing heavily discounted registrations for conferences and seminars, as well as keeping governments with the ability to promote exploration and offer other forms of support to geoscientists seeking work aware of the situation”.
“It’s absolutely essential that geoscientists experiencing tough employment conditions do not lose contact with their profession, peers and colleagues” Mr Erceg said.
“These initiatives by the AIG not only help members to maintain their skills but also provide great networking opportunities which may lead to jobs.
“All AIG members also have access to a dedicated Edumine campus which offers hundreds of high quality, self-paced short courses that, again, enable members to maintain current skills and increase both their awareness of, and ability to apply, new thinking and techniques relevant to their work.
“Members who take advantage of these measures will hopefully be looked on favourably by prospective employers.
“The new information provided by this survey on the type of enterprises that are providing employment for geoscientists and, significantly, undertaking essential exploration to replenish Australia’s resource project pipeline is particularly significant.” Mr Erceg said. “Small companies raise capital from investors to complete a modest program of work to, usually, a very tight budget with little ability to absorb costs imposed by administrative delays and other issues impeding access to land, especially for early stage, very low impact work.
“Every dollar spent on compliance is a dollar not invested in productive exploration to turn geological concepts into discoveries.
“It has been heartening that government agencies in most states responsible for granting exploration title and permitting exploration field work have reported significant reductions in the time required to process applications.” Mr Erceg said. “This has happened, though, at a time of much reduced exploration activity. These functions need to be adequately resourced to prevent current performance from continuing to improve and certainly not deteriorate, as the workload builds with increasing activity in the exploration sector.
“Australia needs its exploration sector to get back to work to help underpin the economic health of our nation and provide opportunities for future generations”.